Incorporating ESL assessments into your lessons is an important way to evaluate your students’ language proficiency and monitor their progress over time. Here are some tips on the best way to craft effective ESL assessments and incorporate them into your lessons.

Only use valid and reliable assessments in ESL
An assessment should be valid and reliable, but what is a valid and reliable assessment in the ESOL classroom?
What is a valid assessment?
A valid assessment should measure the target that it is intending to measure.
Ask yourself, is what we are measuring aligned to what we want to be teaching the students? Don’t measure something that isn’t directly aligned to the learning objectives for the lesson. Revisit your lesson objectives to be sure the assessment directly ties to it.
An example of a valid assessment
For example, if you want your ESL students to be able to discuss what they did yesterday, but you test them by giving them a matching or grammar activity that tests their use of past tense verbs, then did you really test their ability to discuss their activities from the past? You tested a part of the learning objectives, but you didn’t best capture the learning objective. Indeed, they might know all the vocabulary and grammar that they might need to discuss what they did yesterday, and still not be confidently able to pronounce the words in conversation.
You can solve this problem by increasing the validity of the assessment. A more valid assessment might be to interview students one on one and ask them what they did yesterday. Ask them to use 3 verbs in the past tense.
What is a reliable assessment?
In addition to making a valid assessment, it is very important that your assessment is also reliable. A reliable assessment can be replicated by anyone at any time in any location. It gives the instructor a consistent measurement. In other words, if you test a student or someone else tests them, the results should be approximately the same.

Engaging ESL assessment strategies
Recall Challenge using Jamboard (Knowledge board)
How to use a recall challenge: We get a set of instructions . Maybe the student looks at you like a deer in the headlights. Don’t ask “do you understand” because everyone will say yes.
Instead, ask a learned 1. What is the first step, then 2. What is the second step
And then hopefully the student recalls the instructions and tells you
Challenging the brain to recall is a great way to solidify learning. It gets people thinking. You ca use this for vocabulary, grammar, etc. Ask students to pull out the material from their memory
Notice, which areas are they missing? Which areas did they forget? Those are the areas you, as a teacher, needs to focus on
This is a type of Review, but a bottom down review.
This is a brain based learning strategy.
The research shows that reviewing material (such as reviewing notes before taking a test) vs. trying to write down everything you can remember and then reviewing only what you couldn’t recall, the latter is far more effective.
This is an example of a Recall Assessment I completed during a SAABES workshop. It asked me to recall what I rmemebred about Assessments from previous classes. The professional development instructor utilized a whiteboard so we could work in groups on this recall challenge.

Its better to recall and then fill in gaps then to just review everything.
Utilize backward design in your assessments
Think like this: Objectives> assessments> learning activities
Imaging the end of the course. Ask yourself, “What will I hope that students will have learned and still have value two years after they leave?” In other words, what is your vision for the course?
Think bigger than your content.
All your objectives should align with that bigger end result
Make sure you integrate your developing knowledge about assessment into plans for a future unit you intend to teach.

Linguistic Scaffolds for Writing Effective Language Objectives
An effectively written language objective:
- Stems from the linguistic demands of a standards-based lesson task
- Focuses on high-leverage language that will serve students in other contexts
- Uses active verbs to name functions/purposes for using language in a specific student task
- Specifies target language necessary to complete the task
- Emphasizes development of expressive language skills, speaking and writing, without neglecting listening and reading
Sample language objectives:
- Students will articulate the main idea and details using target vocabulary: topic, main idea, detail.
- Students will describe a character’s emotions using precise adjectives.
- Students will revise a paragraph using correct present tense and conditional verbs.
- Students will report group consensus using past tense citation verbs: determined, concluded.
- Students will use present tense persuasive verbs to defend a position: maintain, contend.
Types of ESL Assessments
To write effective assessments for ESL students, you should design and administer all of the following types of assessments. The goal is to identify students’ learning needs and goals; inform instruction and plan differentiated interventions; and, determine and monitor students’ progress toward achieving personal goals and state standards.
Kinds of assessments that have you used in your ESOL instruction
- Needs Assessment
- Formative Assessment
- Summative Assessment
- Standardized Assessment
- Student Self-Assessment
- Student Peer Feedback
What are needs assessments in ESL?
A needs assessment helps you understand whaat your students need. Therefore, a needs assessment should be conducted right at the start. This means, thee best time to conduct your needs assessment is at the student intake appointment, at the beginning of a unit, or at the beginning of an academic year in a class.
If you work for a school or a larger program, then you might already be familiar with needs testing under a different name: placement testing. A placement test or intake test is a type of needs test. Schools often assign them to students to decide what level or class they need to be in.
Examples of needs assessment
- charts with check-
- off boxes
- dot-voting
- “four-corners” activities)
- K, W, L charts
- add how to take class Survey
- fill out Google forms
- Give a personal phone call to ask what they know, what they want to know and need to know in a Private call before class begins . Knowing whether someone ran a business or worked on a farm is a rich trove of information
Needs test for Grammar
You can also give needs test prior to each grammar lesson. For example, The Azar textbook begins each chapter with a Needs asssessment, or as it calls them, a grammar “pretest”. Here is an excerpt below. It tests what students already know in a simple way. It asks them simply decide if the sentence is correct or not. Then, if they got it wrong, they can go to the accompanying chart from the chapter to focus on this area of need. They ddon’t have to learn the entire chapter.

What are formative assessments in ESL?
Formative assessment are called this because they are formative to your lesson. It’s right in the name: they help you “form” your lessons. When used correctly,ensuring they are valid and reliable, they help adjust your teaching methods and immprove your lessons.
Formative assessments are NOT graded, they are different Fromm other types of assessments bc they FOR instructions. They are also informal, used throughout the year to see what students are learning so you can adjust the lessons
Instructors should use throughout the year to see what students are learning so you can adjust the lessons
They are not graded, because their ultimate purpose isn’t to measure the student but to check that your lesson is effective.
You likely utilize formative assessments intuitively and often already. Think of a conversation you are having with a student. Every time you ask them, “does that make sense?” or check in with them, you are implementing a formative assessment. You are checking in to be sure your lesson is landing the way you want it to land. If they don’t understand, you slow down. Iff they understand and fly with the content, the you might adjust the level and make it harder.
Examples of Formative Assessments
- KWL charts
- Think pair-share
- role play activities
- entry/exit tickets
- total physical response activities
- targeted teacher observations
- cloze completions
- vocab matching
- choose the answer tests and quizzes
- comprehension checking questions
- Asking questions that require a complete answer
- Writing assignments (reading responses)
- Grouping students and circulating to listen in on conversation
- Instruction checking questions (i.e. asking them, “Can you explain it to another student who wasn’t here?”)
What are summative assessments in ESL?
Summative assessments are administered towards the end of a learning period to measure how well learners have mastered the essential learning objectives.
Examples of summative assessments
- Interviews with the instructor with a given rubric
- Final projects
- Presentations (powerpoints, google slides, etc.)
How are summative assessments different from formative assessments?
The difference between the types of assessments are what they are used for. The difference between formative assessments and summative assessments is that formative assessments inform your teaching and summative assessments inform your learners about their learning. Sometimes formative assessment can look like summative assessments (a pop quiz for example) but the formative assessment is always used to inform , while the summative is to test the student.
Formative assessment: Comprehension Checking Qs
Formative assessments should be conducted regularly during the lesson to check for understanding
What are standardized assessments in ESL?
What are student self-assessments in ESL?
The purpose of a student self-assessment is to evaluate their personal strengths, to identify gaps in their knowledge or skills, and to build metacognitive awareness. It is not to compare their abilities with other students.
The purpose of a formative assessment is to provide an opportunity for students to reflect on their learning, to monitor the effectiveness of teaching, and to identify gps in student learning. It is not to evaluate learning t the end of a unit in relation to any ELPS.
Student self-assessment builds metacognitive awareness skills
At the end of a lesson, students recap what they learned and what they need to practice more. Self-assessment options vary with language
Examples of student self assessment
-reflective writing prompts
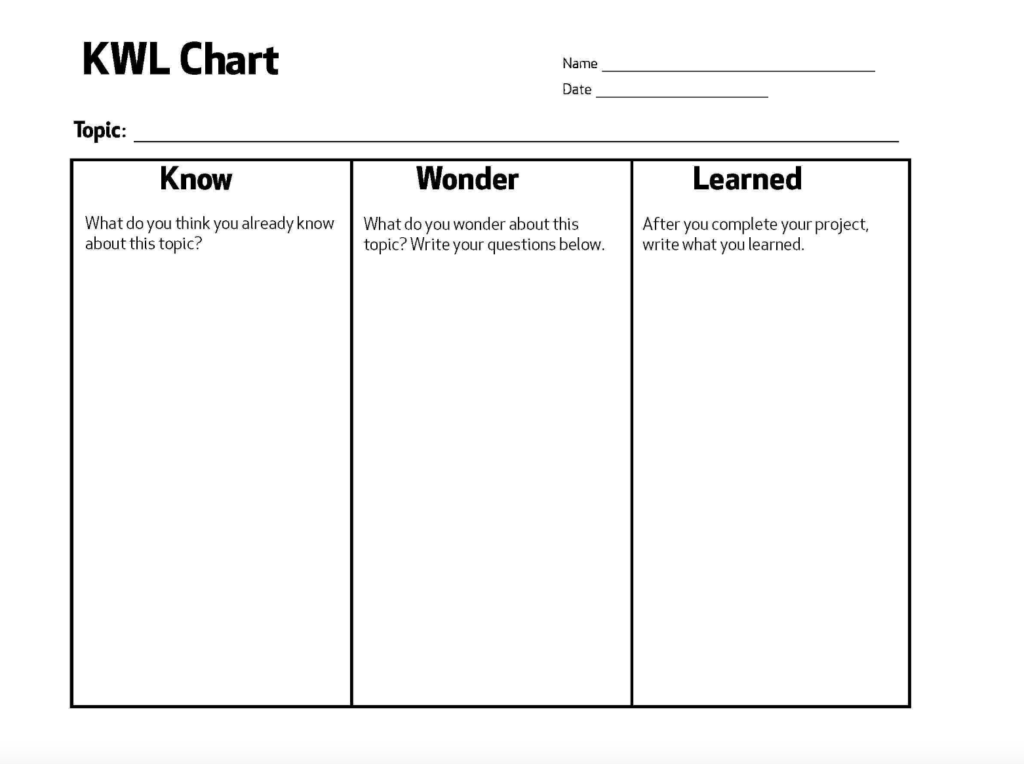
–Using KWL charts.
KWL is an acronym for Know, Want-to-know, and Learned. Creating a KWL chart is an effective way to assess your students needs. It can also be used as a pre-reading, as it helps students read with purpose, and it can be used to generate discussions, too. KWL is easy to apply and can lead to significant improvement in your ability to learn efficiently and to retain what you have learned.
You can find many KWL charts to download online to help you make assessments, such as the one below.
What are student peer feedbacks in ESL?
Peer feedback is the process of having students provide constructive feedback on each other’s language skills, such as writing, speaking, listening, and reading. Peer feedback assessments can be used as a form of formative assessment, where students provide feedback to their peers during the learning process, or as a summative assessment, where students provide feedback after a completed task or project.
In peer feedback assessments, students are typically given clear criteria for what they should be looking for when providing feedback, such as grammar, vocabulary, organization, clarity, and coherence. They are also usually provided with guidelines on how to provide constructive feedback that is specific, actionable, and respectful.
Peer feedback assessments can have many benefits for ESL learners. By providing feedback to their peers, students are able to develop their critical thinking, communication, and collaboration skills. They also gain a deeper understanding of the language by analyzing and evaluating the language used by their peers.
Examples of peer feedback
- peer feedback form
- anonymous reviews
- group discussion (salon style)
Bottom line
To make and use effective assessment, you must apply backward design principles to align assessments to instructional goals, use needs assessments to customize instruction for your student, use formative assessments to gauge student learning and inform instruction, use summative assessments to evaluate learning at the end of a unit. Finally, you must create and implement meaningful feedback and opportunities for learner engagement in assessment activities.
If this interested you, you might also be interested in reading the posts below.
- CCQ: Comprehension Checking Questions
- All About WIDA Standards
- Great Ways to Scaffold while Teaching ESL
“To teach is to learn twice over.”
Joseph Joubert
Learn more
- Teach English online and get paid what you deserve
- My Cambly Review
- Digital Nomad’s Guide: Teaching English Online in Vietnam
- Cruising Through the ABCs: The 5 Stages of Phonemic Awareness
- Best Referral Bonuses in 2023
- Talk the Talk with Cambly